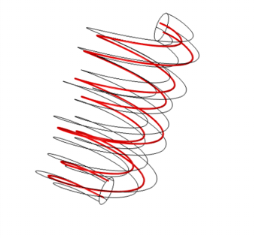
Add a Diffusion Method node to compute the vector field based on Laplace’s equation 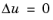 with the vector field v defined as v =
with the vector field v defined as v = 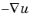 (divided by
(divided by 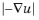 if normalized). This method is a scalar “potential method” resulting in an incompressible vector field and is useful for geometries that are smooth but leads to concentrations at sharp corners. To define the equation in the geometry, you can add the following boundary conditions:
if normalized). This method is a scalar “potential method” resulting in an incompressible vector field and is useful for geometries that are smooth but leads to concentrations at sharp corners. To define the equation in the geometry, you can add the following boundary conditions:
|
|