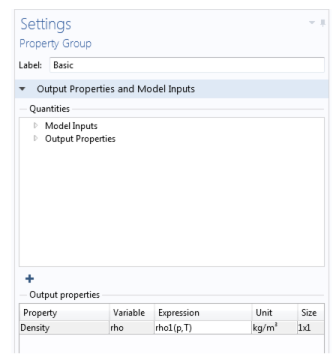
Assume that you want to define the density ρ1 for a material as a function of pressure and temperature: ρ1= ρ1(p, T). You can name the function rho1(p,T) and use the expression p*0.02897/8.314/T to define the function.
|
1
|
On the Materials toolbar, click the Browse Materials
|
|
2
|
Add a Density property to the material.
|
|
a
|
|
b
|
On the Settings window for Material, click to expand the Material Properties section. Under Basic Properties, right-click Density and Add to Material.
|
|
3
|
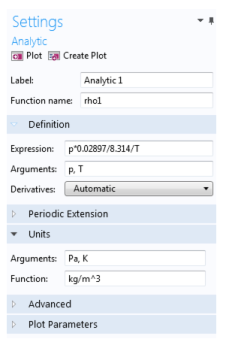
In the Model Builder, under the material node, right-click Basic and select Functions>Analytic. This adds an Analytic subnode (
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Under the Definition section:
|
|
a
|
|
b
|
|
6
|
Under Units:
|
|
a
|
In the Arguments field, enter Pa, K as the units for the pressure and the temperature, respectively.
|
|
b
|
In the Function field, enter kg/m^3 as the unit for the function’s output (density). The function rho1 can now be used to define the density in your material.
 |
|
7
|
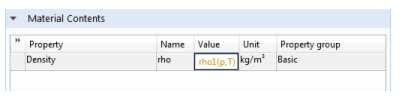
Click the Material node. On the Settings window for Material, under Material Contents, enter rho1(p,T) in the Value column (in the Density row).
 |
Click the Basic node to notice that the Density analytic function is defined on the Settings window for Property Group under Output properties. See Figure 9-9.