In the Model Builder, under Results, right-click Derived Values (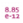 ). Select an option from the list and continue defining each derived value (see Table 20-9).
). Select an option from the list and continue defining each derived value (see Table 20-9).
In the Model Builder, under Results, right-click Derived Values (). Select an option from the list and continue defining each derived value (see Table 20-9).