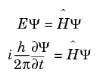The Schrödinger equation (from the Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger) is an equation that describes the behavior of the quantum state of a physical system as it changes in time:
where Ψ is the quantum mechanical wave function (the probability amplitude for different configurations of the system) and 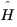 is the Hamiltonian. h, the Planck constant, over 2π is often called the reduced Planck constant (h-bar).
is the Hamiltonian. h, the Planck constant, over 2π is often called the reduced Planck constant (h-bar).